Token Hijack via Unvalidated postMessage Handler and Reflected DOM XSS in Chatwoot Widget Integrations
2025-10-06Found by Patrik Fabian (CEO, HackWare)
Disclosure Timeline
- 2025-05-09 - Vulnerabilities reported via GitHub issues
- 2025-09-06 - Comment on the original issue requesting an update
- 2025-09-22 - Follow-up via email; vendor informed that public disclosure would occur two weeks later if no response is received
- No response received as of 2025-10-06 - Proceeding with coordinated disclosure and CVE request
Vulnerability 1 – Token Hijack via Unvalidated postMessage Handler
Summary
An unrestricted postMessage vulnerability in Chatwoot widget integrations allows attackers to hijack the cw_conversation token via a crafted message. With one click, an attacker can steal this token and retrieve the full conversation history of a victim, potentially exposing sensitive information.
Technical Details
The embedded widget listens to postMessage events without validating the origin of the sender.
A malicious site can send a forged postMessage with the event popoutChatWindow, specifying a malicious baseUrl.
Without validating the message origin, the widget directly calls popoutChatWindow with the supplied baseUrl. This function builds a popup URL that includes the cw_conversation cookie value as a parameter and opens it with a fixed window name (webwidget_session_${websiteToken}). By setting window.name in advance, the attacker can intercept the popup into their own controlled window and capture the cw_conversation token directly from the request URL.
This issue arises from the lack of origin validation in the event listener combined with the insecure handling of the cw_conversation token.
Proof of Concept
The detailed proof of concept (PoC) will not be publicly released at this time. If you are a verified user of Chatwoot’s chatbot widget integration and would like to review the PoC, please contact us at info@hckwr.com.
Impact
- Hijacking of active chat sessions via
cw_conversationtoken - Persistence of access, since the
cw_conversationtoken never expires - Unauthorized access to sensitive conversation data
- Cross-origin abuse through missing origin checks
Solution
The root cause is the missing validation of the postMessage origin and the unsafe propagation of the cw_conversation token into a popup URL. To mitigate:
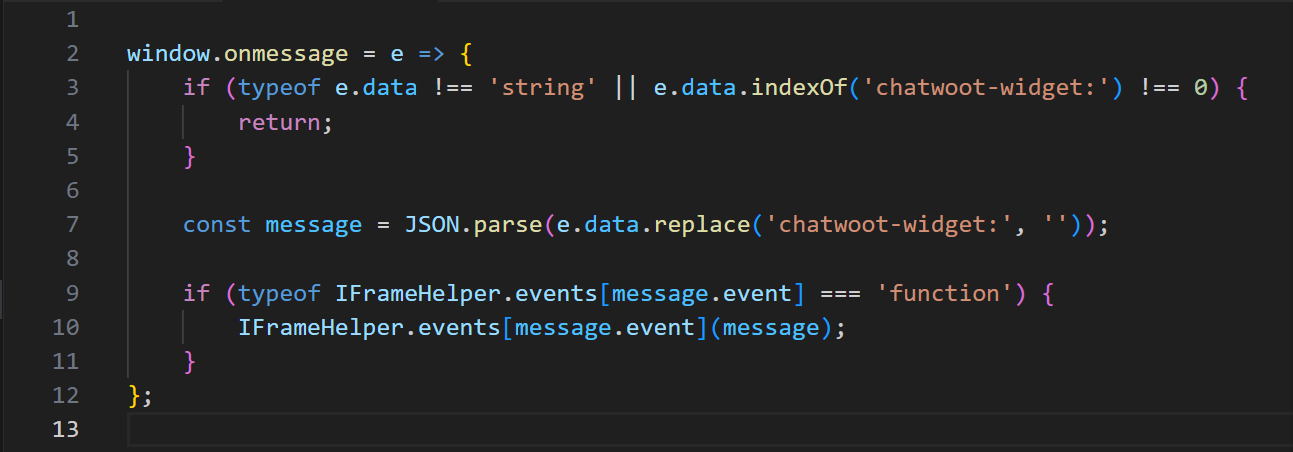
Validate message origin before processing events.
Only accept messages from trusted domains:initPostMessageCommunication: () => { window.onmessage = e => { const trustedOrigins = ['https://<trusted-domain.com>']; if ( typeof e.data !== 'string' || e.data.indexOf('chatwoot-widget:') !== 0 || !trustedOrigins.includes(e.origin) ) { return; } const message = JSON.parse(e.data.replace('chatwoot-widget:', '')); if (typeof IFrameHelper.events[message.event] === 'function') { IFrameHelper.events[message.event](message); } }; };Do not expose sensitive cookies (
cw_conversation) in popup URLs.
Pass only the minimum data required to initialize the widget. Session or conversation tokens should be handled securely (e.g., via HttpOnly cookies or short-lived server-generated tokens).popoutChatWindow: ({ baseUrl, websiteToken, locale }) => { // Removed conversationCookie from being injected into the popup URL window.$chatwoot.toggle('close'); popoutChatWindow(baseUrl, websiteToken, locale); };View source location on GitHub
And in the popup creation:
export const popoutChatWindow = (origin, websiteToken, locale) => { try { const windowUrl = buildPopoutURL({ origin, websiteToken, locale, }); const popoutWindow = window.open( windowUrl, `webwidget_session_${websiteToken}`, 'resizable=off,width=400,height=600' ); popoutWindow.focus(); } catch (err) { console.log(err); } };
Note for developers
If developers do not fix this, every site embedding the widget remains vulnerable. Attackers can trivially hijack active sessions and persistently access conversation history because the cw_conversation token does not expire. This poses a high risk to any deployment.
Vulnerability 2 – Reflected DOM XSS via unrestricted URL of embedded pages
Summary
A reflected DOM-based Cross-Site Scripting (XSS) vulnerability exists in the Chatwoot admin interface. The link parameter inside the URL fragment is directly injected into the iframe src attribute, allowing execution of arbitrary JavaScript.
Technical Details
A link parameter taken from the URL fragment is inserted directly into an iframe’s src attribute without any validation. This can let an attacker run JavaScript inside the iframe or make the iframe load arbitrary external pages, enabling cross-site scripting or phishing.
Proof of Concept
The detailed proof of concept (PoC) will not be publicly released at this time. If you are a verified user of Chatwoot’s chatbot widget integration and would like to review the PoC, please contact us at info@hckwr.com.
Impact
- Execution of arbitrary JavaScript in trusted origin
- Possible theft of authentication tokens
- Phishing or UI redressing within the customer communication platform
Solution (DOM XSS in IframeLoader)
The vulnerability comes from directly binding :src="url" without validation. To mitigate, sanitize the url prop before using it:
<script setup>
function sanitizeUrl(rawUrl) {
try {
const parsed = new URL(rawUrl, window.location.origin);
// Allow only https and same-origin
if (parsed.protocol !== 'https:' && parsed.origin !== window.location.origin) {
return '';
}
return parsed.toString();
} catch (e) {
return '';
}
}
</script>
<template>
<iframe
v-if="url"
ref="iframe"
:src="sanitizeUrl(url)"
class="absolute w-full h-full top-0 left-0"
@load="handleIframeLoad"
@error="handleIframeError"
/>
</template>
View source location on GitHub
Note for developers
If this validation is missing, any attacker-supplied value in ?link= can inject a javascript: payload or external phishing page into the iframe. Sanitization is required at the component level.
Conclusion
Both vulnerabilities - missing origin validation in postMessage handling and DOM-based XSS - allow serious compromise of customer communication data.
As Chatwoot is used in production environments for real customer support, the confidentiality impact is high.
Status: Public disclosure. CVE request in progress.

